The ESG Imperative: Embracing Sustainability for Enterprises

In an era that has seen the drastically growing impact of climate change and has actively started to discuss and make changes to address and mitigate the impact of climate change, individuals, communities, and businesses must adopt sustainable practices to do their part in the movement. Environmental, social, and governance concerns are taking a prominent position in the hierarchy of priorities for investors when evaluating companies.
Illustratively, the "Global Investor Survey 2022" conducted by the professional services firm PwC revealed that robust corporate governance claimed the fourth spot among a roster of ten priorities, garnering a 49% ranking. Similarly, the aspiration to curtail greenhouse gas emissions secured the fifth position with a 44% rating. To effectively tackle the pressing global climate challenge, we must embrace transformational changes rather than mere incremental adjustments.
There is a growing demand from governments, customers, and analysts to comprehend our sustainability policies and initiatives. We have observed an increasing trend in requests for proposals (RFPs) that incorporate inquiries and evaluation criteria pertaining to sustainability credentials and policies, with a particular emphasis on independent certification as evidence. This shift signifies a broader recognition of the importance of sustainability and its correlation to long-term business success.
By prioritizing sustainability in procurement policies, companies can unlock several long-term benefits. This includes minimizing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving resources, and promoting circular economy principles. Simultaneously, integrating sustainability into procurement practices fosters encouragement to find alternative solutions, and encourages collaboration with stakeholders, internal and external, who are also committed to sustainable practices. Sustainability solutions play a vital role in mitigating climate change, preserving ecosystems, and ensuring a better quality of life for present and future generations.
Putting Words into Action: Embracing ESG Initiatives:
Enterprises must be aware of the impact they make on people across the world – including customers, employees, investors, and the wider communities they serve. The primary goal is to create sustained outcomes that drive value and fuel growth while improving the environment and strengthening societies.
A typical ESG framework within an organization would include:
- Diversity, Equity & Inclusion (DEI): Strive to create an inclusive, equitable workplace where every individual's voice is heard and respected. The focus would be on building an inclusive workplace and strengthening diversity through various initiatives.
-
A Gender-balanced workplace where every individual is respected and valued for who they are. The gender diversity charter will focus on a workplace that provides an equitable playing field for all genders in terms of hiring, career growth, and workplace safety.
-
As part of the Generational diversity initiatives, enterprises would continue to strengthen awareness through intergenerational diversity programs, reverse mentoring, and collaboration.
-
As part of the specially-abled charter, organizations could focus on accessible workplaces and technology, progressive hiring policies, sensitization sessions, and creating support communities.
-
-
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): To establish a dedicated social development arm, forging meaningful partnerships to conceptualize and implement projects that solve society's most pressing problems. CSR activities help in uplifting and empowering lives with a bottom-up and collaborative approach while promising long-term commitment to issues and sectors.
-
Governance: Global risk and compliance policies to ensure operations comply with applicable laws, regulations, and ethical standards.
-
Anti-Bribery and Anti-Corruption – Organizations are committed to complying with all the applicable anti-corruption laws, regulations, and policies, and conduct all their business activities with honesty, integrity, and the highest possible ethical standards.
-
Business Conduct & Ethics - This reinforces an enterprise’s core values and drives their attitude towards ethical obligations while fostering a culture of compliance, responsible decision-making, and accountability.
-
Data Privacy - Complying with the applicable data privacy and security requirements, a framework for the protection of personal data that is collected, created, stored, processed, or transmitted within/outside the enterprise.
-
Document Retention – Document storage, retrieval, and destruction policies and processes are crucial to ensure a business runs smoothly and efficiently.
-
Ombuds/Whistle-blower Policy - The Ombuds /Whistle-blower Policy provides a platform that encourages stakeholders having complaints of actual or suspected incidents of unethical practices, or violation of applicable laws and regulations to promptly come forward and express the same without any fear of retaliation.
-
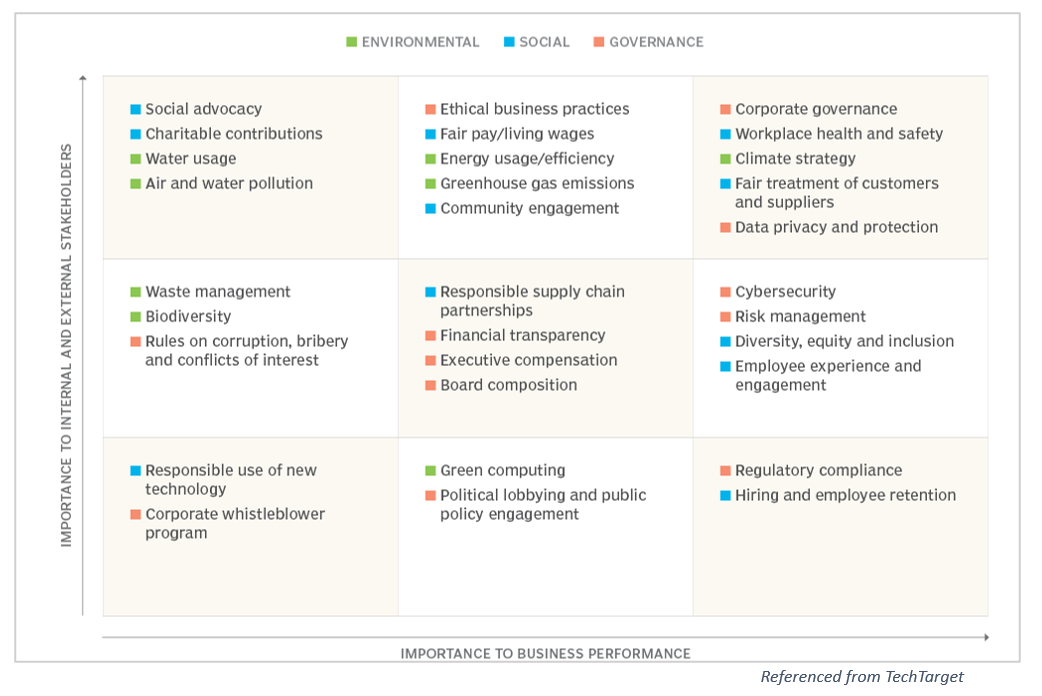
ESG Materiality Matrix
Various organizations have implemented ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) frameworks and standards for business use. Notable entities include the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board, which offers guidance for around 80 industries, the Global Reporting Initiative, the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures, CDP, and the World Economic Forum's International Business Council. Additionally, S&P Global's Corporate Sustainability Assessment allows companies to compare their industry-specific performance.
Mark Thomas, from Escoute Consulting and a co-author of ISACA's 2022 white paper on ESG practices, compared the ESG materiality assessment process to scoping. It's like setting the groundwork to understand and measure how an organization affects ESG matters. Thomas likened the materiality assessment to a blueprint for creating ESG strategies. When doing such an assessment with colleagues, he used a matrix to place important ESG issues. He sorted elements crucial for business success on the horizontal axis and those significant to stakeholders on the vertical axis. This matrix helped pinpoint ESG factors that both business leaders and stakeholders should prioritize.
Driving Sustainable Success
ESG Frameworks compel enterprises to go beyond profit maximization and consider their impact on the planet and the communities they serve. This heightened sense of responsibility not only enhances a company's reputation but also fosters trust among stakeholders, including customers, investors, employees, and regulators.
Integrating ESG considerations into business practices helps identify and mitigate potential risks. Environmental risks, such as climate change impacts or resource scarcity, can significantly affect supply chains and operations. Social risks, such as labor disputes or unethical practices, can lead to reputational damage and legal repercussions. Governance risks, such as weak oversight or lack of transparency, can erode investor confidence. By proactively addressing these risks through ESG measures, enterprises can build resilience and enhance their ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
In today's socially conscious landscape, consumers prefer to associate with brands that align with their values. Enterprises that prioritize ESG considerations and demonstrate a genuine commitment to sustainability can build a stronger brand image and enjoy increased customer loyalty. Engaging in socially responsible initiatives, supporting local communities, and reducing environmental footprints are some ways in which enterprises can enhance their brand value and reputation.
ESG-driven enterprises are more likely to attract and retain top talent. Employees, particularly the younger generations, are increasingly seeking purpose-driven work environments that go beyond financial success. A strong ESG focus demonstrates an organization's commitment to making a positive impact on society and the environment, resonating with employees who want to be part of a meaningful and responsible enterprise. Moreover, ESG initiatives often create a sense of pride and purpose among employees, leading to higher engagement levels and increased productivity.
Digital solutions significantly enhance ESG practices for businesses. They monitor and optimize energy use in buildings, data centers, and manufacturing, including Sustainable Cloud Operations, minimizing the environmental impact of cloud computing. Smart sensors and IoT devices collect real-time data to identify energy-saving opportunities and improve workplace well-being, safety, and hygiene with features like contact tracing and predictive cleaning. The software calculates and tracks carbon emissions, identifying reduction and offsetting strategies.
Digital platforms ensure supply chain transparency, ethical sourcing, and labor practices. They also track diversity metrics, promoting inclusivity. For governments, digitizing citizen services improves accessibility, especially for those with special needs. Robust IT solutions ensure data security, privacy compliance, and risk management. Digital communication tools foster transparent stakeholder communication for better alignment of interests.
Conclusion
ESG considerations have evolved from being a niche concern to a fundamental aspect of business strategy. Embracing ESG principles not only benefits the environment and society but also drives sustainable success for enterprises. From mitigating risks and attracting investors to strengthening brand value and fostering employee engagement, ESG plays a pivotal role in shaping a responsible and ethical corporate identity. By prioritizing ESG factors, enterprises can position themselves for long-term growth, while making a positive difference in the world and leaving a lasting legacy for future generations.