Unlocking the Potential of Distributed Cloud: When and Why Your Business Needs It

In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are continuously seeking innovative ways to scale their operations, improve efficiency, and deliver seamless user experiences. The advent of cloud technology has revolutionized the way organizations leverage their IT infrastructure for business needs and digital transformations. While hybrid and multi-cloud environments have become common in digital enterprises, the need for processing and analyzing data closer to the edge devices and end users is becoming increasingly critical and, in many cases, an advantage.
Consequently, enterprise cloud infrastructure and applications workloads are now being dispersed across public clouds, private data centers, disconnected locations, and at-the-edge devices like IoT endpoints, automobiles, 5G endpoints, and more. This transformation has given rise to what the industry has dubbed the "distributed cloud”. Let's delve deeper into the distributed cloud concept, explore its benefits, and discuss when and why your business would need it.
So, what is a Distributed Cloud?
The distributed cloud is an evolution of traditional cloud computing that focuses on decentralizing cloud resources to bring computation, data storage, and processing closer to end-users and edge devices. In contrast to the centralized approach of conventional cloud models, a distributed cloud architecture aims to enhance performance, speed, reliability, and data sovereignty by extending cloud capabilities to geographically dispersed physical locations. These locations include regional public clouds, customer's datacentres, edge devices, and even disconnected on-premises locations. However, it’s worth noting that the provision of the cloud services, its fabric for operations, governance updates, and evolutions will remain centrally managed by a public cloud provider.
Benefits of Distributed Cloud:
- Enhanced Performance and Latency Reduction: By deploying resources closer to end-users, distributed cloud minimizes data travel time, reducing latency and improving response times for applications and services. This is especially crucial for real-time applications like IoT devices, online gaming, and video streaming.
- Improved Reliability: Distributed cloud distributes workloads across multiple locations, reducing the risk of service disruptions due to single points of failure. If one node experiences an issue, other nodes can seamlessly take over, ensuring high availability and business continuity.
- Improved Data Sovereignty and Compliance: Distributed cloud allows you to keep sensitive data within specific geographic regions to comply with data protection regulations. This helps address data privacy and sovereignty concerns, particularly for businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions. Typical hybrid clouds could also do this to some extent, but distributed cloud helps in difficult scenarios.
- Better Cost Optimization: Distributing workloads strategically can help optimize costs by reducing data transfer expenses and enhancing resource utilization. It enables organizations to adopt a just-in-time and 'just-as-needed' approach, aligning expenses with actual usage.
When Does Businesses Need Distributed Cloud?
There are many use cases where geographical distribution, disconnected locations, and edge devices need to be part of enterprise digital transformations. Let us look at some of them.
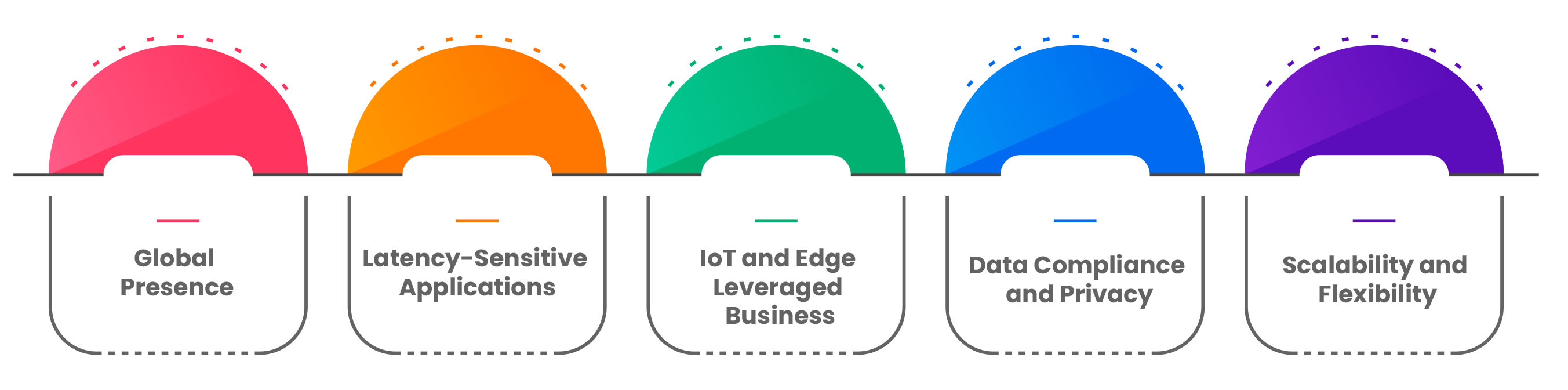
- Global Presence: If your business operates on a global scale, with customers, employees, or partners located in various regions, a distributed cloud can help deliver consistent and reliable services to all users, regardless of their geographic location.
- Latency-Sensitive Applications: If your applications require minimal latency to provide a seamless user experience, such as online gaming, augmented reality, or real-time financial transactions, a distributed cloud can significantly improve performance.
- IoT and Edge Leveraged Business: Businesses that rely on Internet of Things (IoT) devices or edge computing benefit from distributed cloud's ability to process data locally, reducing latency and ensuring real-time decision-making.
- Data Compliance and Privacy: Industries dealing with sensitive data, such as healthcare, finance, or government, can use distributed cloud to adhere to strict data compliance regulations while maintaining control over data residency.
- Scalability and Flexibility: If your business experiences varying workloads or rapid growth, distributed cloud enables you to scale resources quickly and efficiently without compromising performance.
In conclusion, the concept of distributed cloud is a shift in general cloud computing, offering businesses with enhanced performance, improved reliability, and better data control. By strategically distributing resources across various locations, businesses can provide seamless user experiences, adhere to data privacy regulations, and optimize costs. For businesses operating on a global scale, dependent on low-latency applications, or managing sensitive data, delving into the advantages of adopting a distributed cloud architecture can prove highly beneficial. Embracing this paradigm shift could pave the way for your business to thrive in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Today, containerized and serverless workloads orchestrated by Kubernetes empower enterprises to run workloads pretty much anywhere, be it on the cloud, datacentres, disconnected locations, or even at the edge like automobiles. Most hyperscalers now offer multiple services that extend to private data centers and the edge while maintaining the same control plane and fabric as that of the public cloud. They also provide many tools like Azure Arc to facilitate the ease of deployment and management of these complex distributed cloud scenarios.